DESCRIPTION
Overview
HDMIIPECOV2 PRO2 HDMI OVER IP DISTRIBUTION

HDMIIPECOV2 is a budget option for extending HDMI source over network, using MJPEG compression. It supports one to one and one to many operation.
- Extends 1080p HDMI signals up to 120m over single UTP CAT5e/CAT6 cable
- Supports point to point, point to many
- MJPEG compression
- HDCP compliant
- With wideband IR (38-56kHz) control
- Supports TCP/IP protocol
- With mounting ears
- Default TX IP: 192.168.168.55
- Default RX IP: 192.168.168.56
Applications
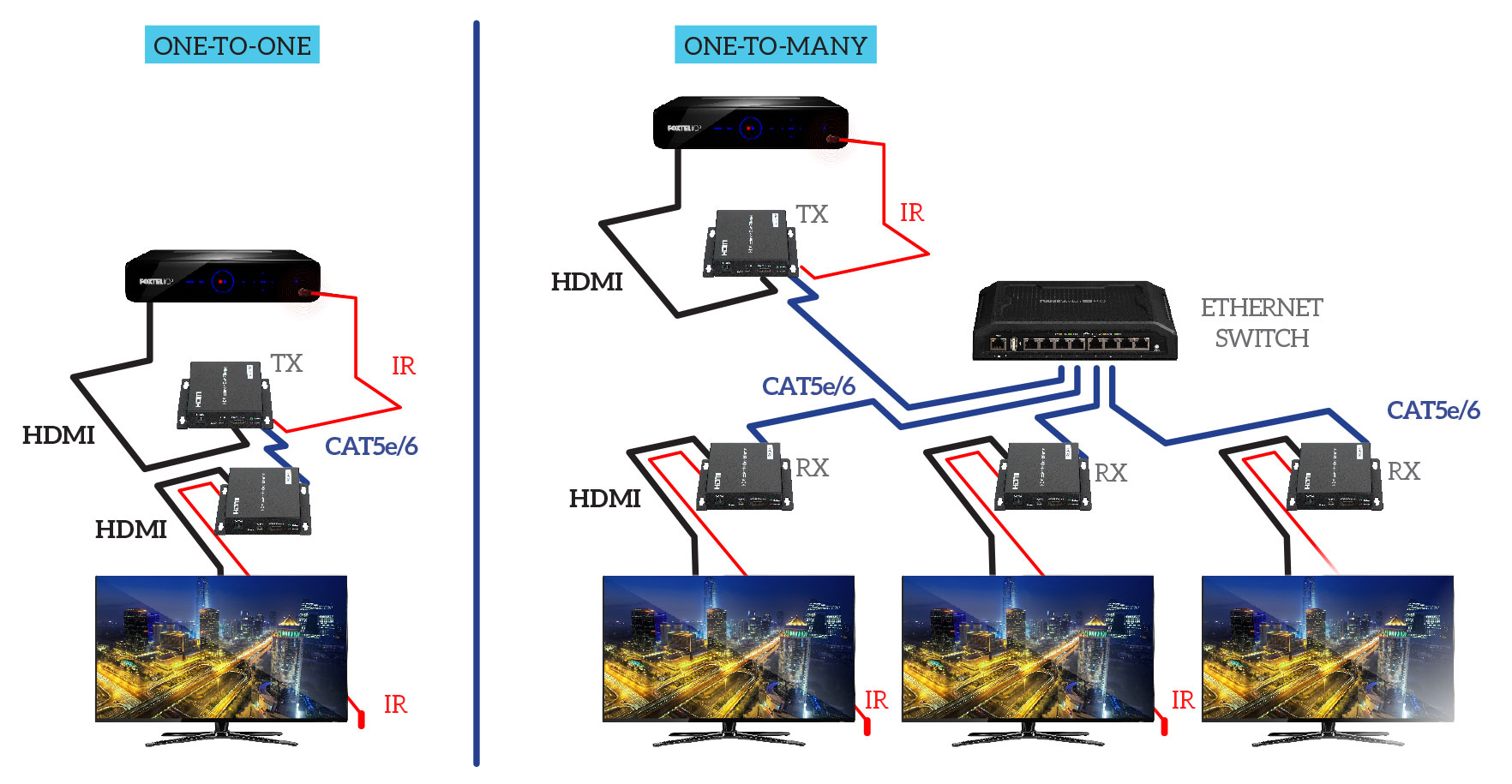
Specifications
Specifications
| Operating Temperature Range | −5°C to 35°C |
| Operating Humidity Range | 5 to 90% RH (No condensation) |
| Input Video Signal | 0.5-1.0V P-P |
| Input DDC Signal | 5V p-p (TTL) |
| Supported Video Format | DTV/HDTV: 480i/480p/576i/576p/720p/1080i/1080p |
| Transmission Distance | 120m: 1080p 8-bit over CAT5e/CAT6 24AWG solid cable |
| Data Bandwidth | 10-90Mbps |
| Power Consumption | |
| Dimension (L×W×H) | 103.5mm × 93.5mm × 24.6mm |
| IR Frequency | 38K-56KHz |
| Net Weight | |
FAQ
FAQ
Is the HDMIIPECOV2 suitable for many-to-many applications?
Yes, however it is not as easy to setup nor is it recommended for reasons explained below:
- The HDMIIPECOV2 uses MJPEG compression which requires very high bandwidth and is likely to saturate your network bandwidth when used in a many-to-many scenario. For this type of application we strongly recommend the Pro2
- HDMIIPPRO which uses H.264 compression that utilises substantially lower bandwidth when compared to MJPEG. The other issue with many-to-many applications is that it requires you have a managed network switch, and set up different VLANs for each transmitter used and then change the receiver IP address accordingly. For example, you set VLAN 1 for Transmitter 1 (eg. Foxtel), VLAN2 for Transmitter 2 (eg. DVD player), when you want the Receiver 1 to pick up the Foxtel, you change the Receiver 1 IP address to the same subnet as VLAN 1 and if you want to display the DVD player, you would change it to the same subnet as VLAN2.


